The ongoing housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue for many Americans, where the dream of homeownership seems increasingly out of reach for a significant portion of the population. Rising home prices and stagnant wages have made it difficult for young families and individuals to find affordable housing options in their desired neighborhoods. Key factors contributing to this crisis include restrictive land-use regulations, which hinder construction productivity and innovation among builders. Often, NIMBY (Not In My BackYard) policies exacerbate the problem by limiting new developments, driving up costs and reducing the supply of affordable homes. As we dive deeper into the current housing market trends, it becomes evident that these homeownership challenges are rooted in broader economic practices that need urgent reevaluation.
The current struggle for accessible housing can be likened to a disparity in the real estate landscape, where many potential buyers face overwhelming homeownership obstacles. Factors influencing this predicament include stringent zoning laws and local opposition to new developments, often referred to as NIMBY dynamics, which have stifled the ability to build affordable homes. As we explore the complexities of this housing accessibility dilemma, it’s essential to consider how construction inefficiencies have paralleled changes in land use policies over recent decades. The historical context reveals that the escalating costs of new homes are not merely a reflection of inflation but a symptom of a decaying construction ecosystem burdened by regulatory constraints. Such systemic issues must be addressed to revive productivity in the sector and foster a more inclusive housing market.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
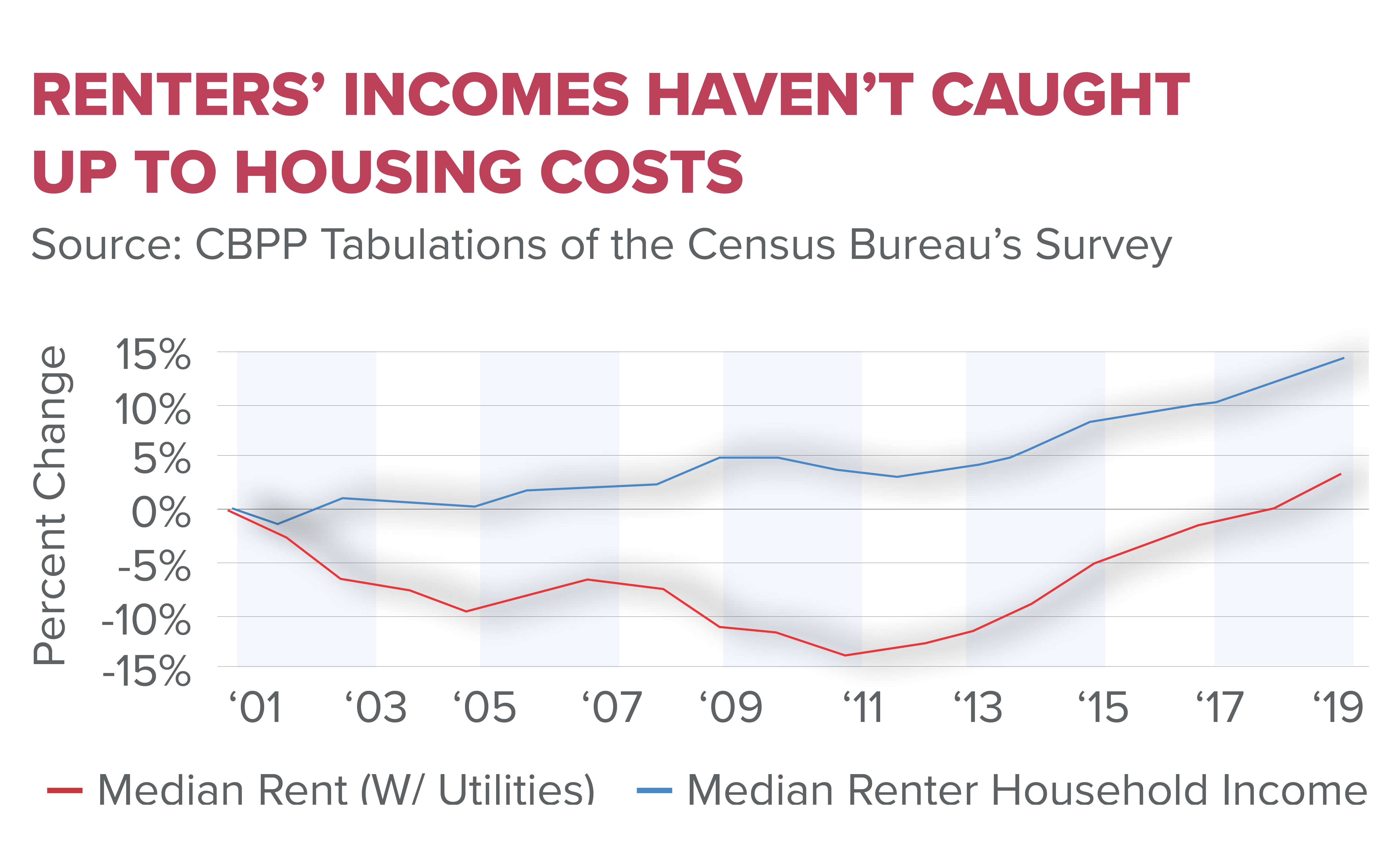
The housing affordability crisis has emerged as a significant issue within the U.S. economy, impacting a large number of Americans seeking homeownership. Rising property prices have outpaced wage growth, leaving many potential buyers unable to afford homes in their desired locations. In fact, the average price of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960, a stark indicator of the challenges facing home seekers today. The intersection of stagnant wages and soaring prices has made the dream of homeownership increasingly unattainable for diverse segments of the population.
Additionally, the crisis has been exacerbated by the influx of stringent land-use regulations and NIMBY policies, which have restricted the development of new housing. When communities prioritize maintaining neighborhood aesthetics over increasing housing supply, they unintentionally further heighten affordability issues. This has resulted in a construction landscape where builders face greater hurdles and increased costs, ultimately translating into higher prices for prospective homeowners.
The Impact of Land-Use Regulations
Land-use regulations play a crucial role in the housing affordability crisis by limiting the scale of new construction projects. These regulations often result in smaller, bespoke developments rather than large-scale housing initiatives, which can benefit from economies of scale. As noted in recent studies, the number of homes produced per construction worker has declined significantly post-1970, coinciding with a surge in regulatory constraints. This shift has been detrimental not just to builders but also to consumers in the housing market who seek affordable options.
Furthermore, the evidence suggests that the reduction in construction productivity has broader implications for the housing market. As builders navigate a maze of regulations—from lot sizes and densities to design approvals—they are deterred from engaging in innovative building practices. This serves to stagnate the potential for advancements in construction technology and reduces construction output, compounding the existing affordability crisis and thereby stifling the housing market’s growth.
NIMBY Policies and Their Consequences
NIMBY, or ‘Not In My Back Yard’ policies, have increasingly gained prominence in discussions surrounding housing and urban development. These community-driven movements often oppose large-scale construction projects, which are critical for addressing housing shortages. As communities resist development for fear of altering their neighborhood character, they inadvertently limit the opportunities for new housing stock, further straining affordability.
The consequences of NIMBYism are particularly felt in urban areas where housing demand is high yet supply is restrictive. As a result, essential workers and individuals from diverse backgrounds face challenges in accessing quality housing. The demand for affordable housing continues to grow, yet the ability to meet this demand diminishes as local regulations tighten, manifesting in significant economic disparities and limiting the options available to prospective homeowners.
Construction Productivity and Economic Growth
The decline in construction productivity is a critical factor linked to the broader economic landscape. Historically, the construction sector has exhibited high productivity levels, contributing positively to economic growth. However, recent trends show a stark reversal; productivity in construction has stagnated while other industries have thrived. An analysis of Census data reveals that the number of homes produced per worker has declined sharply since the 1970s, indicating a systemic issue within the housing sector that requires urgent attention.
This decline in productivity can be attributed to factors such as reduced economies of scale resulting from increased regulatory hurdles and the decreasing size of construction firms. Larger firms that have the ability to innovate and implement cost-saving technologies are now less prevalent in the market. As construction productivity lags, the housing market faces difficulties adapting to the growing demand for affordable housing, further exacerbating the housing affordability crisis.
The Future of Homeownership
Homeownership remains a vital aspect of the American dream, yet it is increasingly out of reach for many. With rising prices and stagnant wages, prospective buyers are facing unprecedented challenges. The issue is compounded by factors such as land-use regulations and community opposition to new developments that could provide needed inventory to the housing market. This disconnect between supply and demand has led to a decline in homeownership rates among younger generations, creating long-term economic implications.
Looking ahead, the future of homeownership relies on addressing the obstacles impeding housing supply. Implementing more flexible land-use policies and fostering community engagement in the development process may help encourage new projects while addressing residents’ concerns. By prioritizing affordable housing solutions, policymakers can work towards revitalizing the housing market, ensuring that homeownership remains a viable option for future generations.
Innovation in Construction
Innovation has historically been a driving force in the construction industry, enabling builders to increase efficiency and reduce costs. However, recent trends suggest a decline in patenting and innovation within the sector compared to manufacturing. This stagnation can be linked to the restrictive land-use regulations and the small size of many current construction firms, which do not have the resources or incentive to invest in new technologies and methods.
Encouraging investment in construction innovation is crucial for revitalizing the housing market and improving housing affordability. By fostering an environment conducive to research and development, builders can explore innovative solutions such as modular construction and prefabrication techniques. These strategies not only have the potential to lower costs but also to increase productivity, ultimately benefiting consumers seeking affordable housing options.
Rethinking Community Development
Community development must evolve to address the pressing issues of housing affordability and construction productivity. Traditional models of development often prioritize short-term gains and resident acceptance over long-term sustainability and economic growth. To tackle these challenges, it is essential for communities to adopt new planning strategies that focus on comprehensive growth while incorporating diverse housing options.
Engaging stakeholders from all corners of the community can help to balance the needs of current residents with those of prospective homeowners. Workshopping new models of collaborative development can foster understanding and pave the way for necessary housing developments that meet the needs of the growing population. By embracing a more inclusive approach to community development, the barriers between residents and developers can be lowered, leading to improved housing affordability.
The Role of Economics in Housing Policy
Economic theories provide crucial insights into housing markets and the factors influencing supply and demand. Understanding the intricate relationship between land-use regulations, labor costs, and consumer demand is essential for developing effective housing policies. By analyzing past trends and current challenges, policymakers can formulate strategies that promote sustainable development while addressing the urgent need for affordable housing.
An economic perspective emphasizes the importance of supply-side solutions to increase housing availability and affordability. This includes revisiting zoning laws, reducing regulatory burdens, and fostering competitive market conditions that encourage builders to deliver homes at various price points. Comprehensive economic research can elucidate the drivers of the housing market, offering actionable steps toward resolving the ongoing housing affordability crisis.
Challenges to Affordable Housing Initiatives
Affordable housing initiatives face a myriad of challenges that hinder their effectiveness. High land prices, combined with stringent regulations and community opposition, create a complex landscape for developers seeking to provide lower-cost housing options. Many of these initiatives struggle to secure funding and community support, which are critical components for their success. As policymakers strive to implement and sustain affordable housing projects, they must navigate these intricate challenges.
Moreover, the competition for available land and resources often leads to lengthy project timelines, increasing costs and deterring investment. As a result, potential residents remain in a state of uncertainty as they navigate the complexities of finding affordable housing. Bridging the gap between developers and community interests is key to overcoming these challenges and ensuring that affordable housing initiatives can thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the housing affordability crisis and how does it relate to housing market trends?
The housing affordability crisis refers to the increasing difficulty for many Americans to afford homeownership due to rising housing prices outpacing income growth. This trend has been influenced by various housing market trends, including escalating land-use regulations and NIMBY policies that limit new construction, thereby reducing supply and driving up costs.
How do land-use regulations contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations can exacerbate the housing affordability crisis by restricting the size and scale of housing developments. These regulations often result in smaller projects that have higher per-unit costs, reducing overall housing supply and making it harder for potential homeowners to find affordable options.
What are NIMBY policies, and how do they impact the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY policies, or ‘Not In My Backyard’ attitudes, lead to community resistance against new housing developments. This resistance can inhibit construction, resulting in a shortage of homes and driving up prices. As a consequence, NIMBY policies play a significant role in the broader housing affordability crisis.
How does construction productivity affect the housing affordability crisis?
Declining construction productivity has adversely affected the housing affordability crisis by increasing the costs of building new homes. When the construction industry is less productive, it produces fewer units at a higher cost, which contributes to the overall housing shortage and increases home prices.
What challenges do prospective homeowners face due to the housing affordability crisis?
Prospective homeowners face numerous challenges due to the housing affordability crisis, including sky-high property prices, limited housing inventory, and rising mortgage rates. These factors make it increasingly difficult for many to achieve homeownership as affordability continues to decline.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The cost of new homes has more than doubled since 1960, making ownership unattainable for many Americans. |
| Role of Land-Use Regulations | NIMBY policies have limited large construction projects, decreasing productivity in the building sector. |
| Productivity Decline | Between 1970 and 2000, construction productivity fell by 40% despite overall economic growth. |
| Comparison with Manufacturing | While manufacturing productivity has increased, housing construction has stagnated since the 1970s. |
| Generational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are seeing a significant decline in housing wealth compared to older generations. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that significantly impacts many Americans today. With housing prices more than doubling since the 1960s, many are unable to achieve homeownership. This situation is exacerbated by strict land-use regulations that stifle innovation and increase costs, preventing builders from developing affordable housing at scale. While other sectors have thrived, construction has lagged, creating a barrier for young people to accumulate wealth through homeownership. Addressing the housing affordability crisis requires a reevaluation of these regulations to foster a more productive construction environment.